Specifications
Description#
Runtime service is in charge of the workspaces execution depending on declared triggers, such as : events, dates or HTTP.
Technical stack#
| Library | Role | Version |
| Express | HTTP framework | 4.21 |
| express-openapi-validator | Swagger-based syntax validation of incoming requests | 5.3 |
| @prisme.ai/broker | Message broker interface | latest |
Design#
Events & API#
Produced events :
- runtime.webhooks.triggered
- runtime.schedules.triggered
- runtime.automations.executed
- runtime.automations.scheduled
Performance & Scalability#
Below are the results of differents performance tests conducted on this testing automation :
simpleUserJourney:
name: performance testing automation
when:
endpoint: true
do:
- set:
name: name
value: Doe
lifespan: "2"
- conditions:
"{{name}} == Doe":
- emit:
event: apps.test
payload:
lastName: John
default:
- emit:
event: apps.newtest
payload:
lastName: Smith
output:
content: "{{name}}"
requestBody: "{{body}}"
set, a conditions block testing this variable and an emit.
During these tests, the runtime instances were connected to :
- A 2vCPU / 4GB MongoDB replicaset
- A 1vCPU / 1GB single-node redis
MongoDB primary node never exceeded 7% CPU and 30% Memory usage.
Redis never exceeded 5% CPU and 4% Memory usage.
Testing script :
import http from 'k6/http';
import { check, group, sleep } from 'k6';
export const options = {
stages: [
{ duration: '5m', target: 100 }, // simulate ramp-up of traffic from 1 to 100 users over 5 minutes.
{ duration: '10m', target: 100 }, // stay at 100 users for 10 minutes
{ duration: '5m', target: 0 }, // ramp-down to 0 users
],
thresholds: {
'http_req_duration': ['p(99)<1500'], // 99% of requests must complete below 1.5s
'webhook run successfully': ['p(99)<1500'], // 99% of requests must complete below 1.5s
},
};
const BASE_URL = 'https://api.eda.prisme.ai';
const USERNAME = 'someAccountEmail';
const PASSWORD = 'someAccountPassword';
const WORKSPACE_ID= "someWorkspaceId"
export default () => {
const webhookRes = http.post(`${BASE_URL}/v2/workspaces/${WORKSPACE_ID}/webhooks/Automation`, {
foo: "too"
});
check(webhookRes, {
'webhook run successfully': (resp) => resp.status === 200,
'is body present': (resp) => resp.json().hasOwnProperty('body'),
});
sleep(1);
};
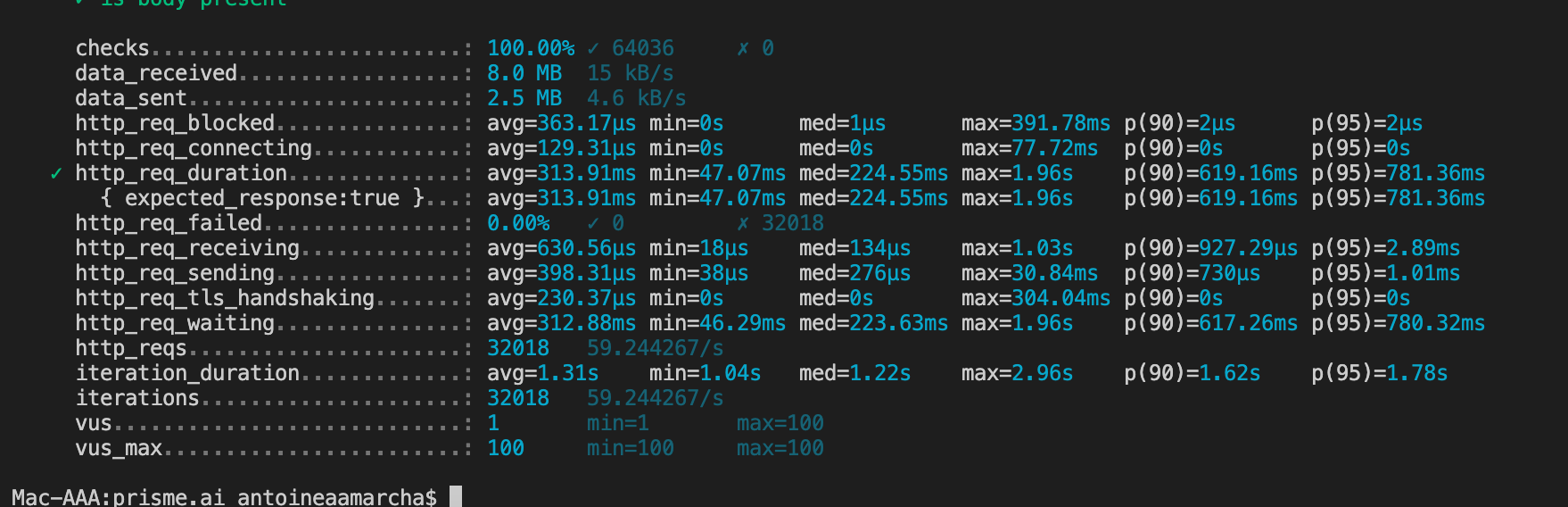
Scenario 1 : 100 concurrent users during 10 minutes, 1 runtime/events/api-gateway instance#
The 100 concurrent users gradually reached their maximum number during the first 2 minutes, then stayed at that level during 5 minutes, before gradually decreasing during 2 minutes.
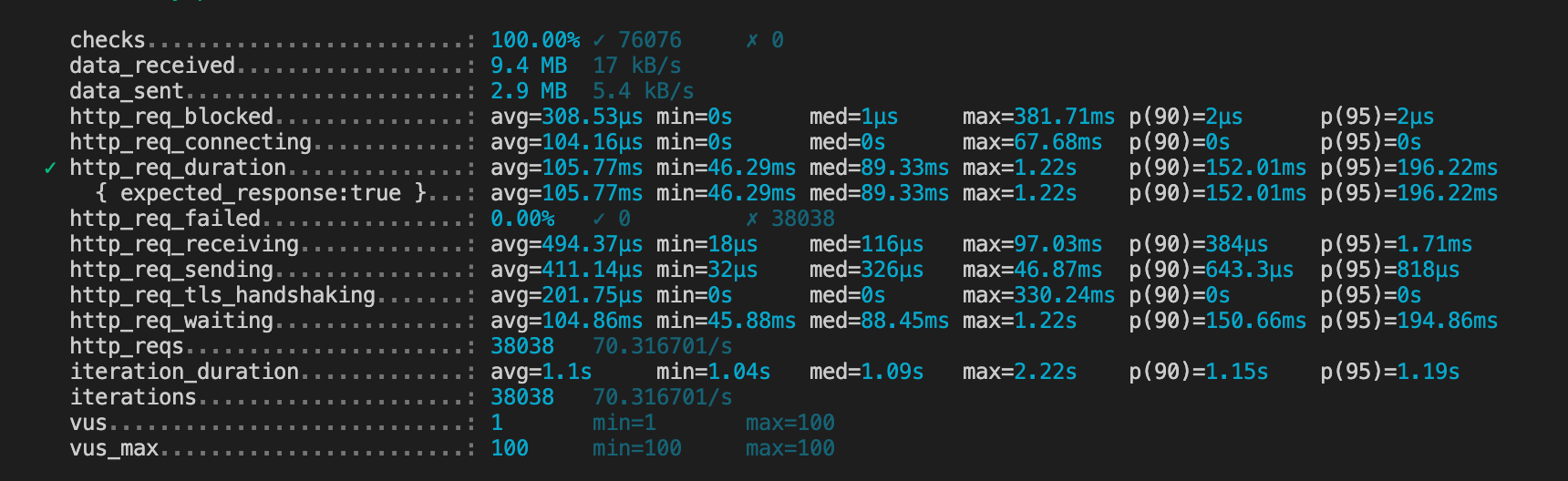
Scenario 2 : 100 concurrent users during 10 minutes, 2 runtime/events/api-gateway instances#
The 100 concurrent users gradually reached their maximum number during the first 2 minutes, then stayed at that level during 5 minutes, before gradually decreasing during 2 minutes.
Limits & Constraints#
| Feature | Limit type | Value | Action if exceeded | Comments |
| Automation execution | Number of successive automation execution for a same correlationId | 20 | The 21th event is ignored in order to stop the chain | Configurable with MAXIMUM_SUCCESSIVE_CALLS env var |
| Contexts | Memory space (in KB) used by all the contexts in one workspace | 10 KB | Once the limit reached, any set instruction is skipped until the admin frees memory with delete |
Quality#
Development standards and quality measurement#
The required quality level corresponds to the recommended SonarQube Quality Gate:
- 80% minimum code coverage
- 3 % max of duplicated lines
- Level A in Maintabily, Reliability and Security
Logs#
Any action is logged into two different ways:
- Trace of the HTTP call if there is one (produced at the Gateway API level)
- Transcription of the action as an event (produced by the service handling the action)
In both cases, all the usual contextual information is included (provided by the common bootstrap between the backend services).\ As a minimum, this information should include : :
- Correlation id
- User id
- Workspace id
- Timestamp
- Log criticality
Errors#
Technical errors (aka unexpected errors) such as a timeout on a REST service call are caught by the service and logged with the full stack trace.
If this error occurs during the processing of an HTTP request, the caller simply receives a generic "Internal Error".
In addition to the error logs, the error is also transmitted as a generic error event.
Both in the log and in the event, the usual contextual information is included as much as possible (see Logs).
Supervision#
Just like the other backend micro services, this one provides different administration routes:
- /metrics : Prometheus
- /sys/logging : dynamically change log details
- /sys/heapdump : Generate a memory dump that can be retrieved from the instance and loaded into Chrome for easy debugging
- /sys/healthcheck : Returns a code 200 if the instance is "healthy"
Linting#
The code should be formatted using Prettier, using the version specified in the package.json